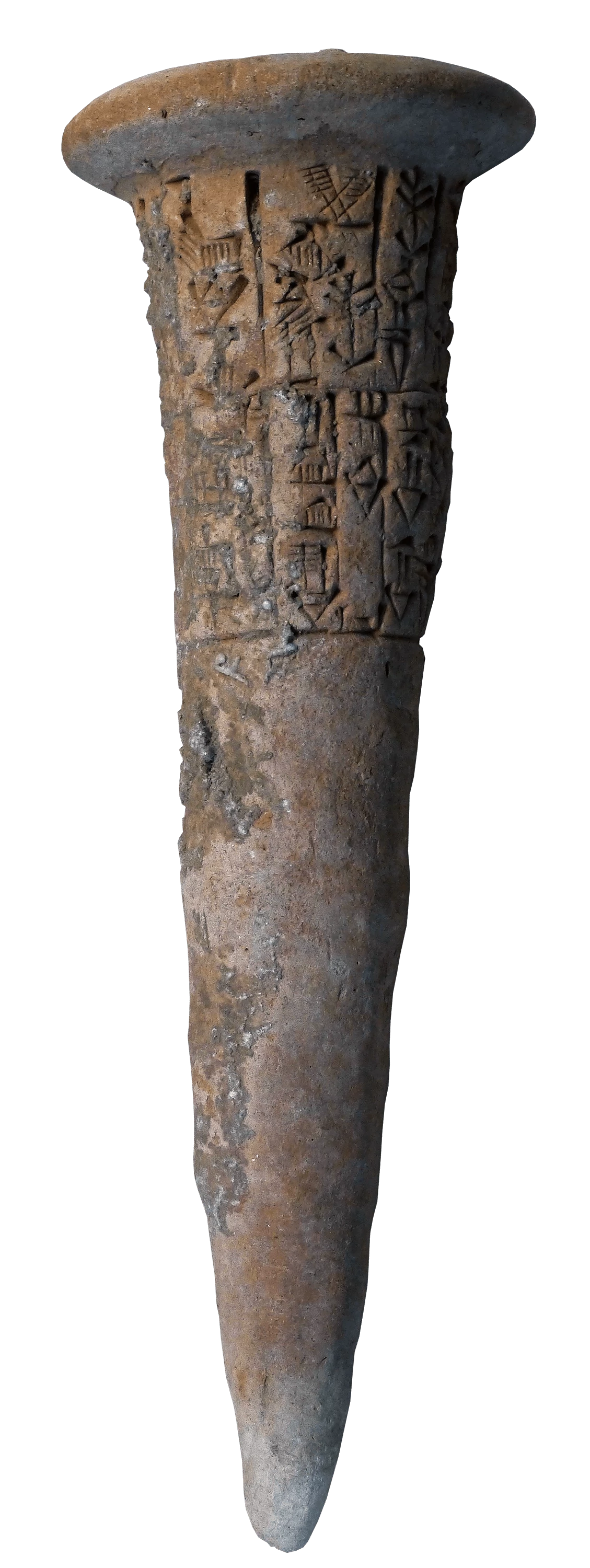
Clay Nails, a Treaty of Fraternity 2400BCE

Cone of Entemena 2400BCE
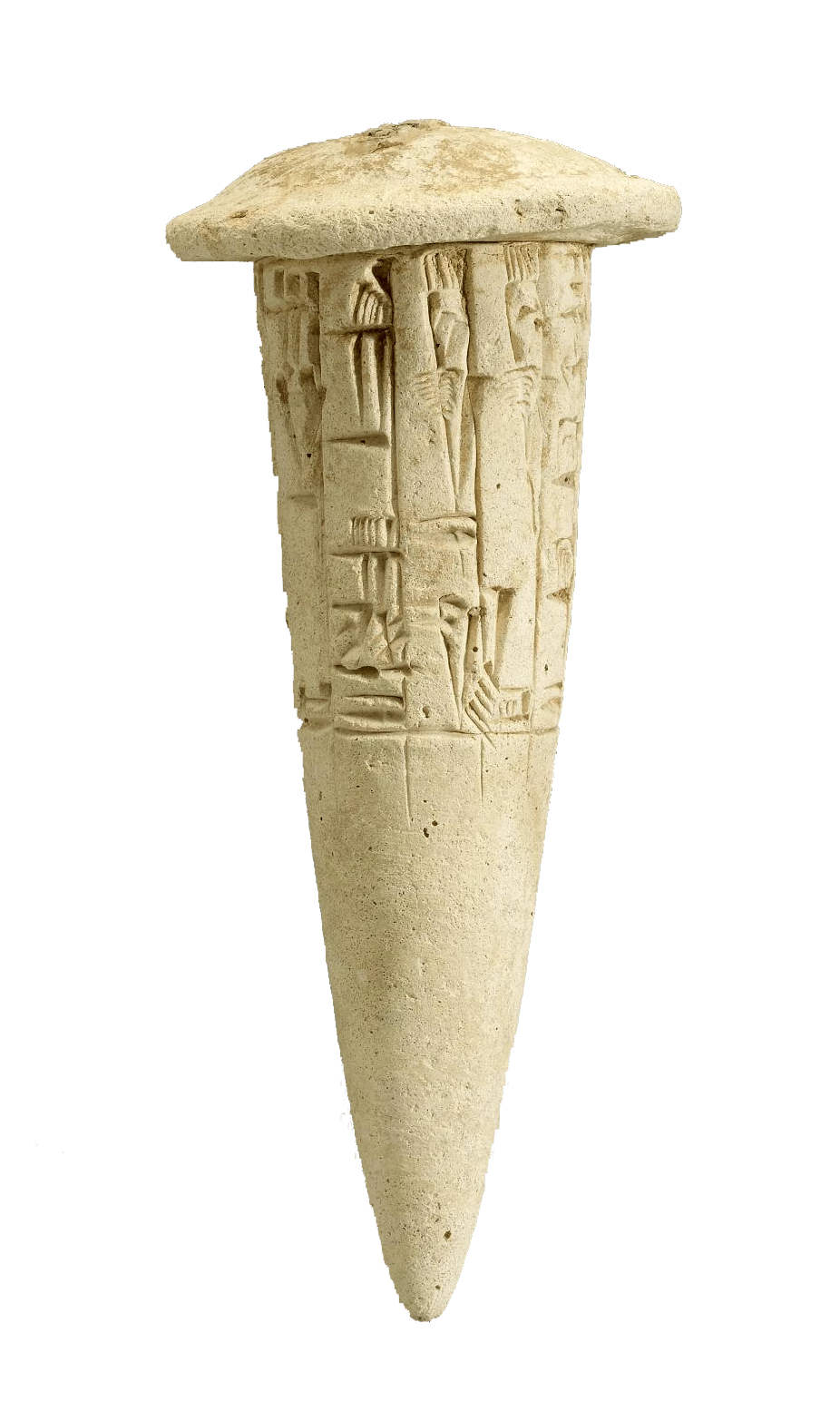

Dedication Nail 2100BCE
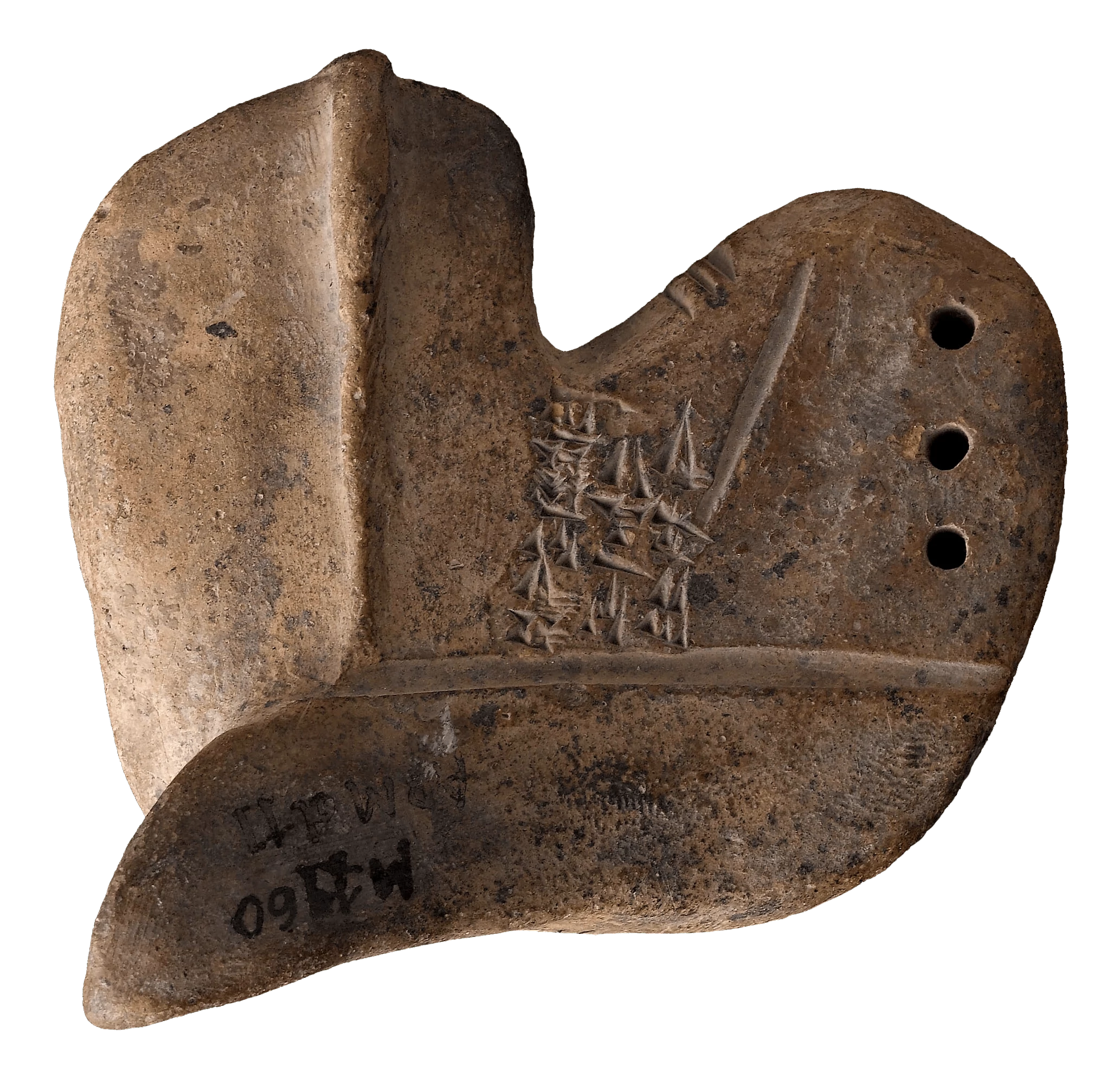

Divination Liver Model: Omen of siege 2000BCE
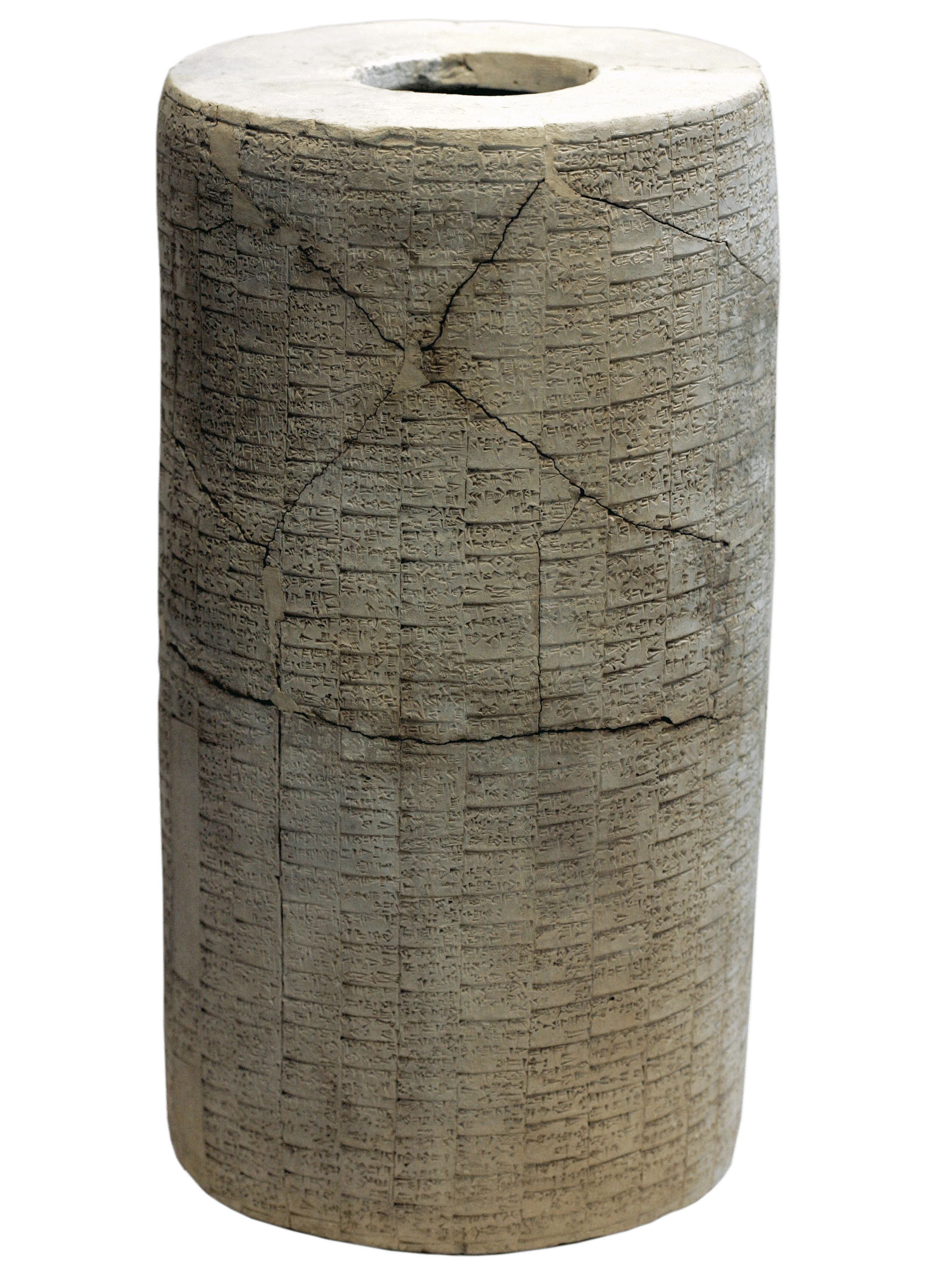

Gudea cylinders 2125BCE
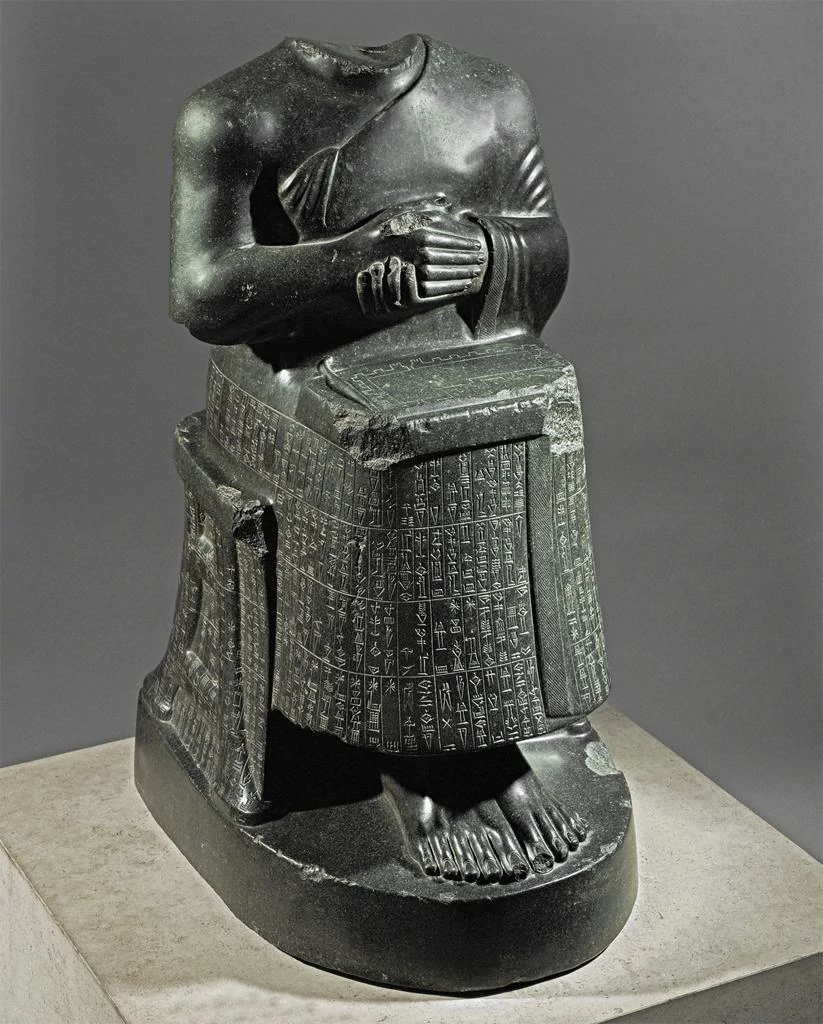

Gudea Diorite Sculpture 2120 – 2120BCE
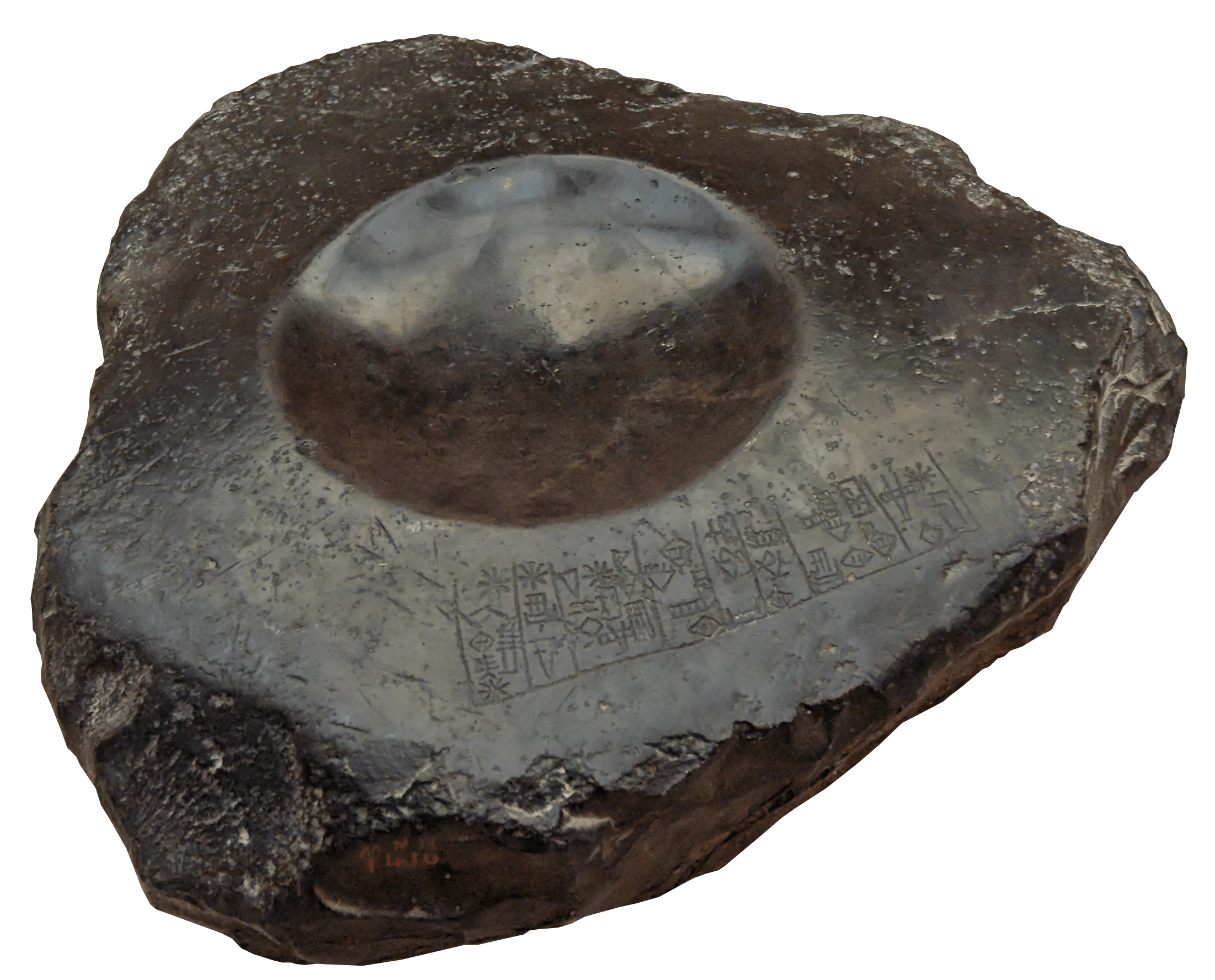

Hinge inscripted with Entemena 2400BCE

Hymn to Iddin-Dagan 1950BCE

Inscription by Naram-Sin: Temple Construction 2250BCE
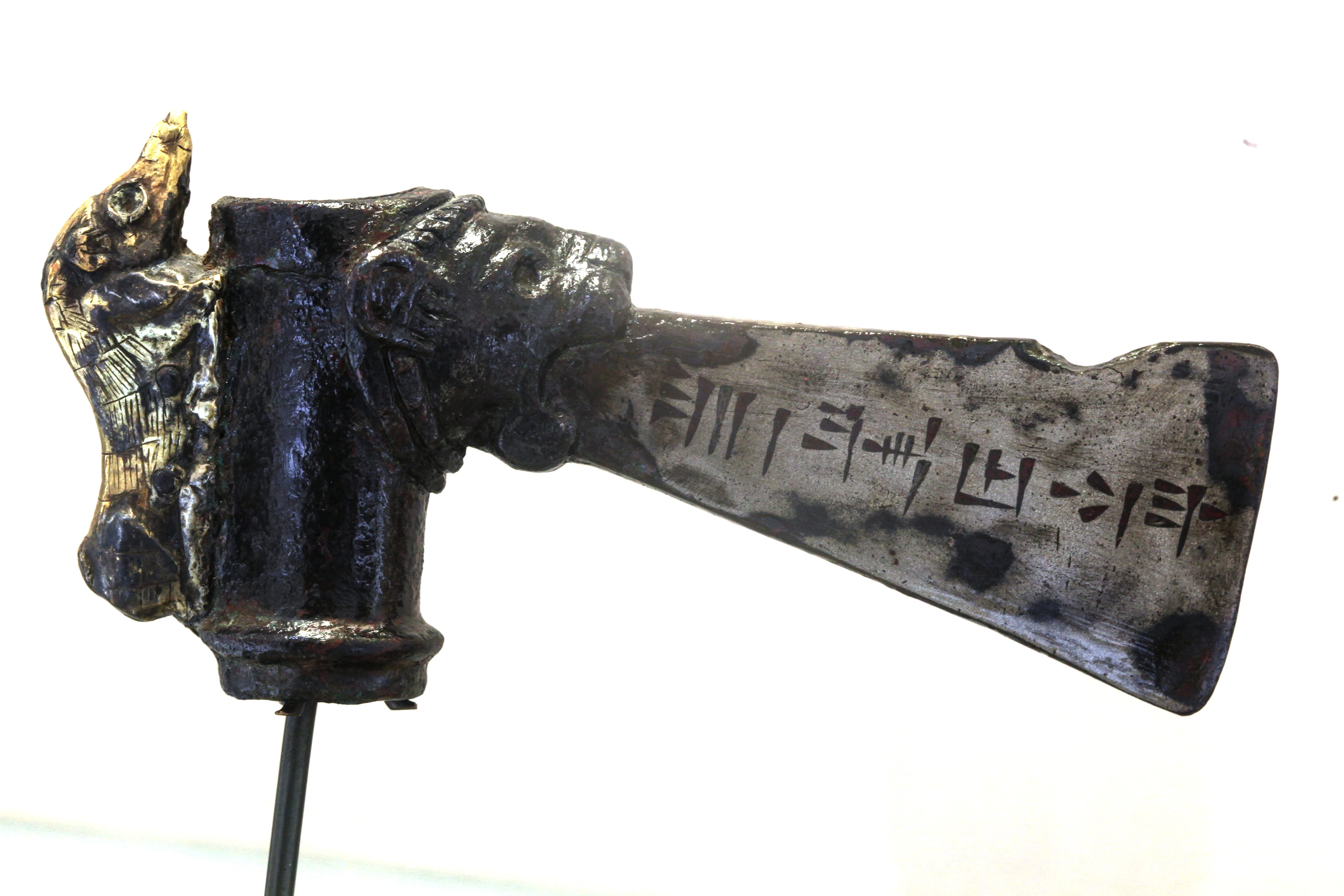

King Untash-Napirisha Axe Head 1300BCE

Prologue to Law Code of Hammurabi 1780BCE
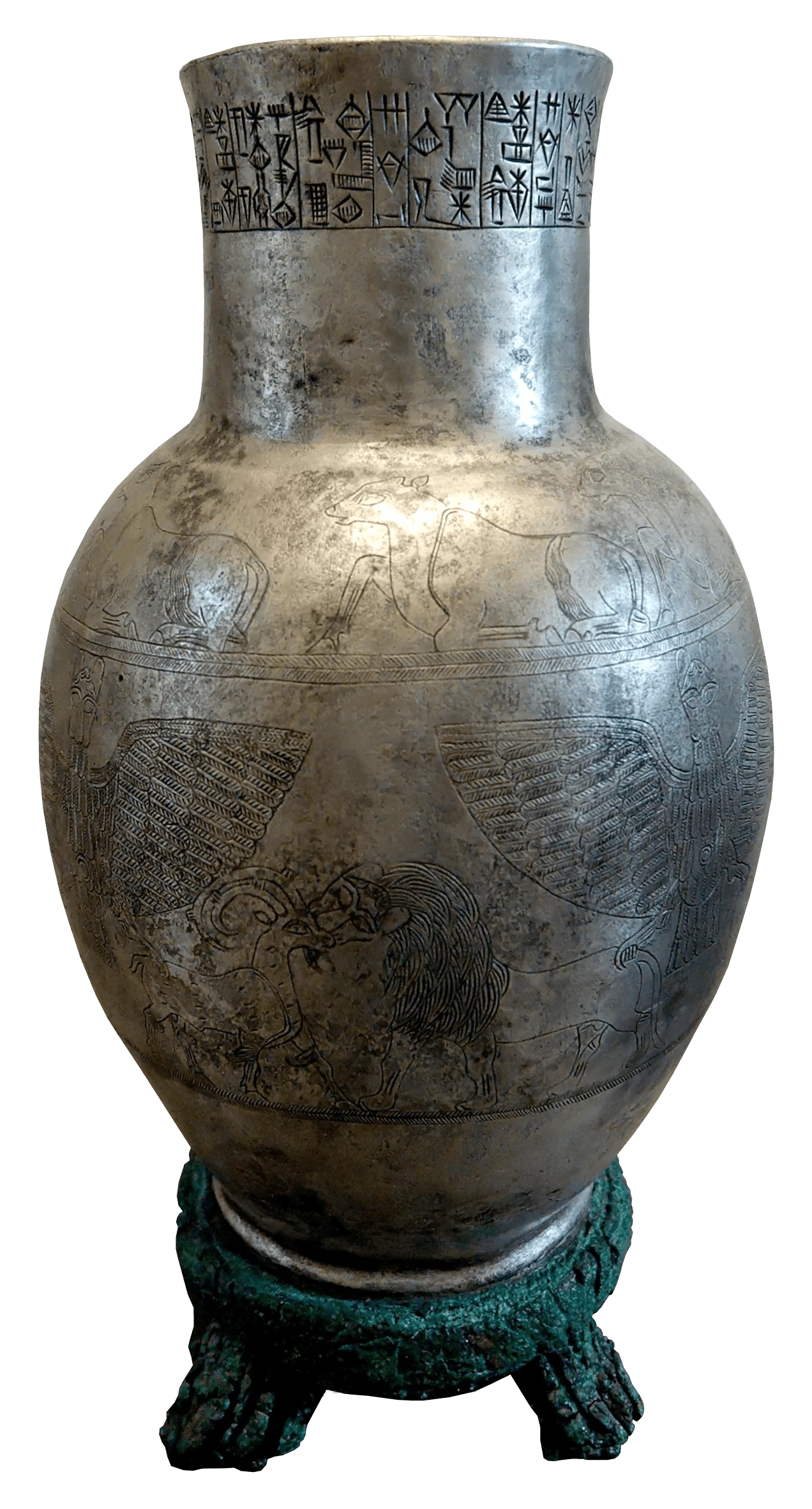

Silver Vase with Cuneiform 2400BCE
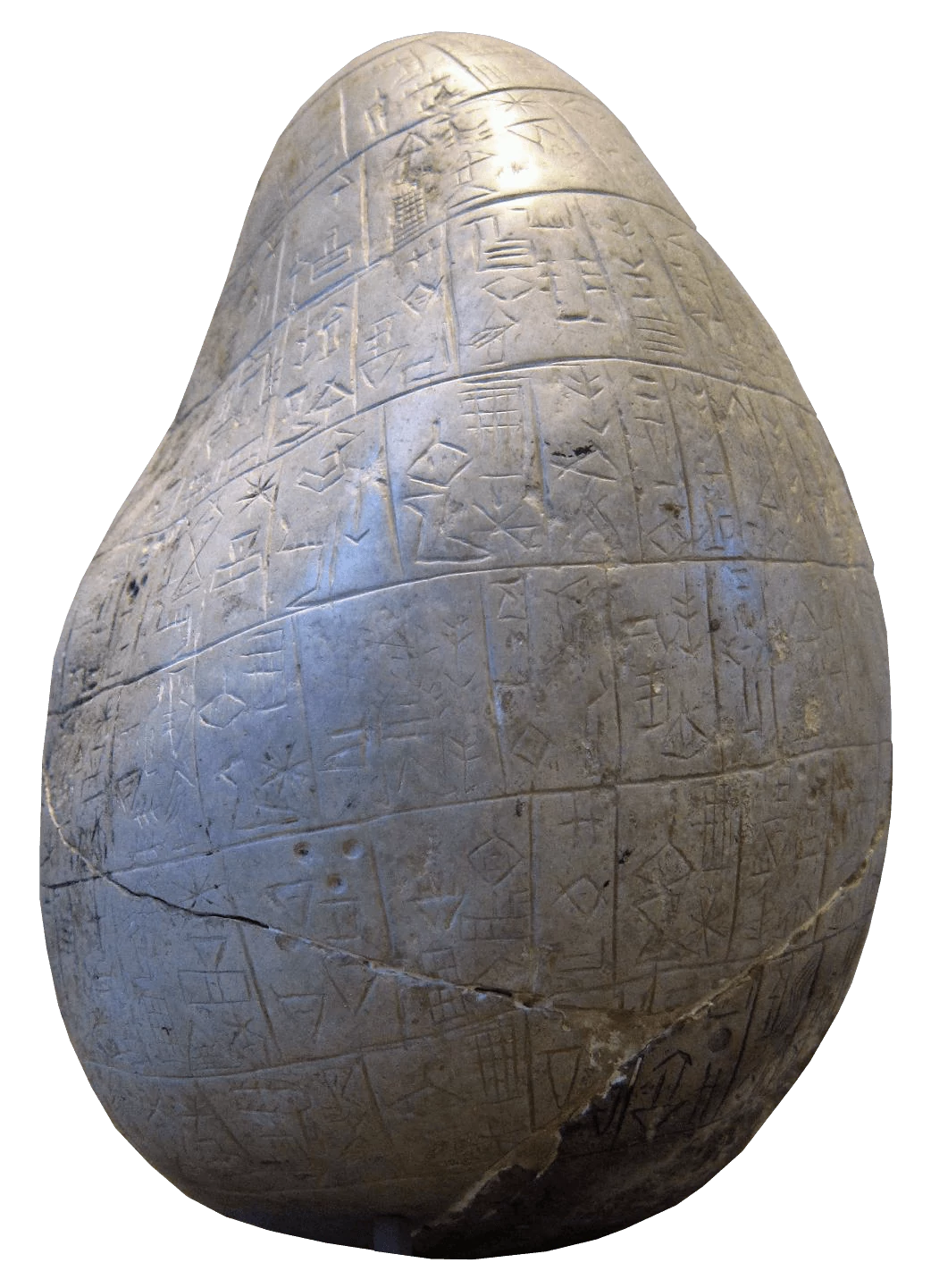

The Eannatum Boulder 2450BCE

The Gilgamesh Flood Tablet 700BCE